Machines That Sip, Not Guzzle
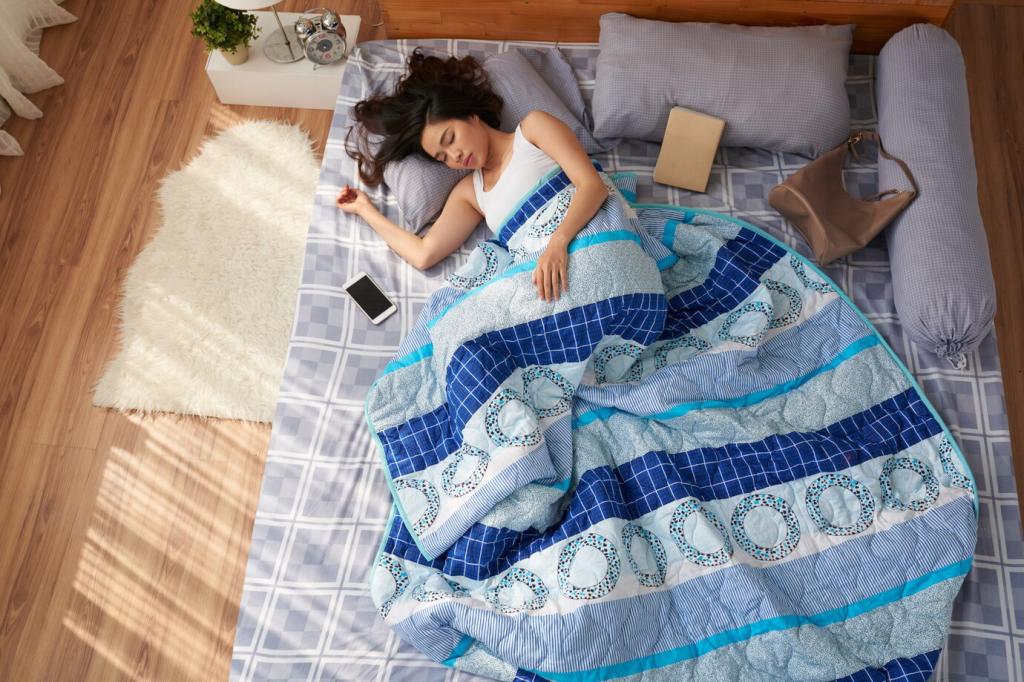
Upgrading to premium-efficiency motors, paired with variable frequency drives, reduces electrical load and provides gentler starts. Stable speeds protect filament integrity and limit breaks, preventing energy wasted on rethreading and unplanned downtime.
Machines That Sip, Not Guzzle
Sensors and closed-loop control keep tension steady, minimizing breakage and reprocessing. Consistency shortens cycle times and lowers average power draw per kilogram of yarn, all while delivering a more uniform, luxurious finish.